In the world of water management systems, the significance of a well-functioning foot valve cannot be overstated. Expert David Johnson, a respected authority in hydraulic engineering, emphasizes, "A quality foot valve is crucial for maintaining consistent water flow and preventing backflow in any pumping application." This statement underscores the essential role that foot valves play in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of water flow control systems.
Foot valves are designed to allow water to flow in one direction while preventing it from flowing back, thus protecting pumps and maintaining prime. Understanding the various options available can greatly impact the performance of your water systems. With a variety of designs and materials, choosing the right foot valve can enhance system efficiency and longevity, ultimately leading to better resource management.
In this article, we will explore the top ten foot valves on the market, highlighting their unique features and advantages. By examining these options, we aim to provide insights that will assist you in selecting the optimal foot valve, tailored to your specific needs and system requirements. This guide will serve as a valuable resource for anyone looking to optimize their water flow control strategies.

Foot valves play a crucial role in various water systems, serving as a one-way valve installed at the bottom of a pump or suction line. These valves are essential for maintaining water flow and preventing backflow. When the pump operates, the foot valve opens, allowing water to flow into the suction line. Once the pump is shut off, the foot valve closes, creating a seal that prevents water in the suction line from draining back into the source, thereby ensuring that the system remains primed and ready for the next operation.
In addition to facilitating uninterrupted water flow, foot valves also contribute to system efficiency and longevity. By preventing air from entering the lines, they help maintain the necessary pressure for optimal pump performance. Moreover, foot valves come in various designs, offering different functionalities. Some incorporate a strainer to filter out debris, while others may have a weighted mechanism for better sealing. Understanding the specific functionalities of foot valves is essential for selecting the right type for each unique application, ultimately leading to more effective water management and reduced maintenance needs in water systems.
| Foot Valve Model | Material | Size (Inches) | Max Pressure (PSI) | Flow Rate (GPM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | PVC | 1 | 150 | 25 |
| Model B | Brass | 1.5 | 200 | 30 |
| Model C | Stainless Steel | 2 | 300 | 50 |
| Model D | Cast Iron | 2.5 | 250 | 60 |
| Model E | Aluminum | 3 | 180 | 70 |

When selecting a foot valve for your water control systems, several key features are crucial for optimal performance. One of the primary considerations is the valve material. Foot valves are typically made from durable materials such as bronze, PVC, or stainless steel. Data from recent industry reports indicate that stainless steel models exhibit superior corrosion resistance, making them particularly suitable for environments with aggressive water chemistry. In fact, over 60% of professionals in the field recommend stainless steel for both longevity and reliability, especially in agricultural and industrial applications.
Another vital feature to evaluate is the valve size and flow rate capabilities. The diameter of the foot valve should match the piping system to ensure efficient water flow without excessive pressure loss. According to the American Society of Civil Engineers, an incorrectly sized valve can result in flow reductions of up to 30%, adversely affecting system efficiency. Additionally, look for foot valves equipped with a reliable sealing mechanism to prevent backflow when the pump is off. Reports suggest that foot valves with elastomeric seals provide a tighter closure, significantly reducing the chances of water siphoning back into the source, which can lead to equipment damage or contamination. By considering these features, you can ensure that your foot valve selection will enhance the performance and reliability of your water control systems.
Efficient water flow is crucial for the optimal performance of various systems, whether in irrigation, plumbing, or industrial applications. Foot valves play a significant role in achieving this efficiency by allowing water to flow in one direction while preventing backflow. Their design helps maintain a consistent water level in suction lines and ensures that pumps do not lose their prime. By selecting the right foot valve, users can ensure smoother operation and reduce the risk of equipment damage caused by water fluctuations.
When considering foot valves for efficient water flow, factors such as size, material, and installation method are essential. A proper size ensures that the valve fits the pipeline without creating unnecessary restrictions. Materials like PVC, brass, and stainless steel offer varying levels of durability, depending on the application environment. Additionally, understanding the flow capacity and the specific demands of your system can lead to better performance. Selecting the correct foot valve promotes effective water management, thus enhancing overall system functionality and longevity.
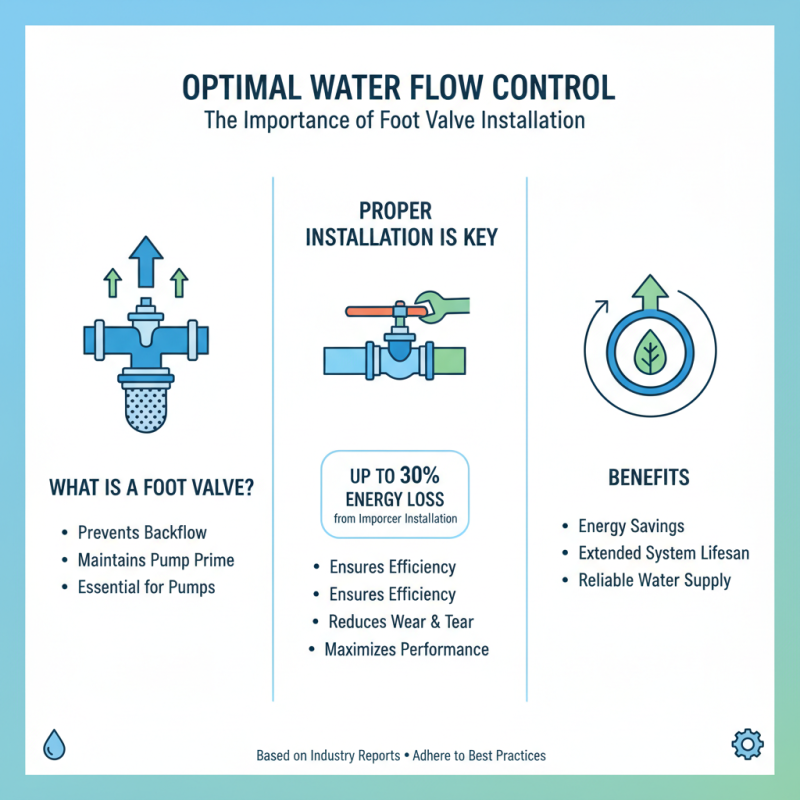
When it comes to ensuring optimal water flow control in your systems, the installation and maintenance of foot valves are paramount. While these components are essential for preventing backflow and maintaining prime for pumps, proper installation can significantly impact their performance. According to industry reports, improper installation can lead to up to 30% energy loss in pumping systems, underscoring the importance of adhering to best practices during setup.
**Tips for Installation:**
- Ensure that the foot valve is placed at a depth that minimizes debris accumulation. This can be achieved by positioning it at least two feet above the bottom of the tank or water source.
- Use a correctly sized valve to match the intended flow rate and pressure. A mismatch can cause inefficient water flow and potential damage to the system.
- Double-check the sealing of the valve after installation to prevent water leakage that might compromise suction.
Maintenance is equally crucial for sustaining the longevity and efficiency of foot valves. Regular inspections to clear any debris and verify the integrity of seals can prevent issues before they escalate. According to a survey conducted by hydraulic experts, about 20% of reported valve failures were directly linked to lack of maintenance, emphasizing the need for routine checks as part of standard operational procedures.
**Tips for Maintenance:**
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule to inspect foot valves for wear and tear, ideally every six months.
- Clean screens and strainer components regularly to ensure unimpeded water flow.
- Replace any damaged or corroded parts promptly to maintain system integrity and prevent costly repairs in the future.
Foot valves play a crucial role in maintaining water flow in systems by preventing backflow and ensuring a steady supply. However, these essential components can encounter common issues that disrupt their functionality. One prevalent problem is clogging, often caused by debris or sediment accumulation. When a foot valve is clogged, it may not open properly or may restrict water flow, resulting in inadequate pressure to the rest of the system. Regular inspections and maintenance can help mitigate this issue, and using a strainer can further protect the valve from unwanted particles.
Another issue that can arise with foot valves is wear and tear, leading to leaks or failure to seal. Over time, the components of a foot valve, such as the seat and the flapper, can deteriorate due to constant exposure to water and the elements. If you notice water seeping around the valve when the pump is off, it may indicate sealing problems that need immediate attention. Replacing worn parts or, in some cases, the entire foot valve can restore optimal performance. Additionally, ensuring the valve is installed at the correct depth can help prevent pressure-related issues, ensuring that it operates efficiently for longer periods.